What Is the Difference Between Interferential and Microcurrent Therapy?
Modern families are always looking for ways to be healthier and more independent. One of the best methods is through treatments such as interferential therapy and microcurrent therapy. But what is the difference between interferential and microcurrent therapy?
This article will provide an in-depth look into both therapies, compare their differences, and give readers actionable advice on which one might work better for them or their family members. By learning about these two distinct approaches to physical wellness, modern families can take a step forward toward achieving greater health independence. So let’s answer together: what is the difference between interferential and microcurrent therapy?
Table of Contents
Interferential Therapy
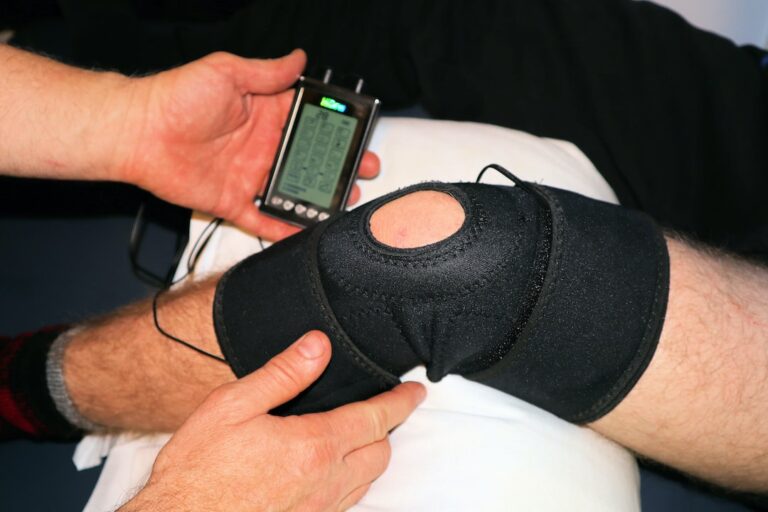
Interferential therapy is an electrotherapy treatment that uses low-frequency alternating current (AC) for therapeutic purposes such as reducing muscle spasms or increasing local blood flow to relieve chronic pain conditions like arthritis or sciatica.
Benefits of Interferential Therapy
The primary benefit of interferential therapy is its ability to reduce chronic pain caused by various conditions including osteoarthritis, tendonitis, bursitis, fibromyalgia, and more.
Additionally, it has been shown to increase joint flexibility while decreasing swelling in areas where there may be inflammation due to injury or disease processes such as rheumatoid arthritis.
It can also be used for post-operative rehabilitation as well as helping patients recover from sports injuries faster than traditional methods alone would allow them to.
How Does Interferential Therapy Work?
During this procedure, two electrodes are placed on the affected area, sending out AC pulses at different frequencies that interfere with each other. This creates a sensation similar to massage but without any physical contact between the patient and therapist.
This helps relax tense muscles while promoting better circulation within those tissues leading to less discomfort during movement activities afterward.
In addition, these currents have been found effective in blocking nerve impulses associated with certain types of chronic pains, allowing patients relief from their symptoms when nothing else seemed able to beforehand.
(Source)
Microcurrent Therapy
Microcurrent therapy is a type of electrical stimulation used to treat pain and inflammation. It works by sending very low-level electrical currents through the skin to stimulate the nerves and muscles.
This can help reduce pain, improve circulation, and promote healing. The current used in microcurrent therapy is much lower than that used in traditional electrotherapy treatments such as TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation).
Benefits of Microcurrent Therapy
The benefits of microcurrent therapy include:
- Reduced muscle tension.
- Improved range of motion.
- Increased blood flow to the area being treated.
- Decreased swelling and inflammation.
- Enhanced healing time for injuries or wounds.
- Relief from chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia or arthritis.
- Reduction in scar tissue formation after surgery or injury.
Additionally, it is beneficial for those suffering from headaches/migraines due to its ability to relax tense muscles around the head and neck areas
How Does Microcurrent Therapy Work?
During a session with a trained practitioner using microcurrent therapy equipment, electrodes are placed on specific points on your body where you’re experiencing discomfort or injury. These electrodes send out tiny pulses which provide electrical stimulation to the underlying tissues at various depths depending on how strong they are set during treatment sessions.
This helps increase circulation while reducing inflammation and promoting healing within these areas over time when done regularly enough.
Interferential vs Microcurrent Therapy
Both interferential therapy and microcurrent therapy use small electric currents to stimulate nerve fibers to reduce pain, improve circulation, reduce inflammation, increase the range of motion, decrease muscle spasms, and promote healing.
What Is the Difference Between Interferential and Microcurrent Therapy?
The main difference between these two therapies lies in their frequency levels. Interferential therapy uses higher frequencies than microcurrent therapy does.
This means that it can penetrate deeper into tissue but also carries more risk of side effects such as skin irritation or burns if not properly monitored. Microcurrent therapy has lower frequencies so it is less likely to cause any adverse reactions but may not reach deep enough into tissue for certain conditions.
Additionally, treatment sessions with interferential therapy typically last longer than those with microcurrents due to their higher intensity level while microcurrent treatments tend to be shorter in duration because of their lower intensity level.
Finally, cost-effectiveness can vary depending on whether you choose interferential or microcurrent therapies since each type requires different equipment and supplies which will affect overall costs associated with treatment sessions.
Which Is Better: Interferential or Microcurrent Therapy?
What is the difference between interferential and microcurrent therapy? Which is better?
Both interferential and microcurrent therapies have been proven effective for treating chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia, arthritis, sciatica, carpal tunnel syndrome, and tendonitis. However, there isn’t one definitive answer as to which one is better since both treatments offer different benefits depending on individual needs and preferences.
When Is Interferential Therapy Better than Microcurrent Therapy?
In general terms, interferential current therapy may be better suited for treating acute muscle spasms or strains due to its ability to penetrate deeper into tissue layers than microcurrent therapy can reach.
In addition, interferential therapy also offers an advantage over microcurrent because it produces less heat during use. This makes it safer overall compared to MCT treatments especially when being applied near sensitive areas like joints where high temperatures could cause further damage if not monitored closely.
When Is Microcurrent Therapy Better Than Interferential Therapy?
In general, microcurrent therapy is best suited for treating chronic issues such as fibromyalgia or arthritis because it provides longer-lasting results than interferential. Its ability to penetrate deeper into tissue layers where inflammation may be present without causing any discomfort or side effects is also a plus.
Additionally, since microcurrents don’t cause involuntary muscle contractions, they can provide targeted treatment without affecting surrounding areas. This makes them ideal for treating specific localized areas such as neck pain or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Finally, due to its lower intensity compared to interferential current treatments, it requires fewer sessions making it more cost-effective over time when dealing with chronic issues.
How to Find an Interferential or Microcurrent Therapy Session
Now we have answered: what is the difference between interferential and microcurrent therapy? Once you’ve made an initial decision on which therapy to pursue, you need to find a provider.
Finding an interferential or microcurrent therapy session can be a daunting task. With so many options available, it’s important to do your research and find the right provider for you.
Here are some tips on how to find an interferential or microcurrent therapy session that is best suited for your needs:
Ask Your Doctor For Referrals
If you have already been diagnosed with a condition that could benefit from either type of therapy, ask your doctor if they know any providers who offer these services in your area.
Many doctors have relationships with local therapists and may be able to provide referrals based on their experience working with them in the past.
Additionally, asking friends or family members who have used similar treatments can also be helpful when searching for a qualified therapist near you.
Check Credentials and Licenses
When researching potential providers, make sure they are licensed by the state board where they practice as well as certified by professional organizations such as The American Physical Therapy Association (APTA).
Additionally, check out online reviews from other patients who have received treatment from the same provider. This will give you insight into their level of care and customer service before scheduling an appointment yourself.
Schedule a Consultation
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of potential providers, schedule consultations with each one so you can get more information about their services firsthand before deciding which one is right for you.
During these consultations, ask questions about their approach towards treating specific conditions like yours as well as inquire about payment plans or discounts offered at their clinic if applicable. This way, there won’t be any surprises later on down the line!
Conclusion
What is the difference between interferential and microcurrent therapy? Interferential therapy uses a high-frequency current to stimulate nerve fibers and reduce pain while microcurrent therapy uses low-level electrical currents to promote healing and tissue repair.
While both therapies can be effective in treating certain conditions, it is important to understand which one will work best for you before beginning treatment. Ultimately, the decision should be made with your healthcare provider based on their assessment of your individual needs.