How Do I Know If My Microbiome is Healthy? Tips & Signs
How do I know if my microbiome is healthy? The significance of our gut health in overall wellness has been made increasingly apparent, thus prompting the query as to how one can determine if their microbiome is healthy. In this comprehensive guide, you will delve into the fascinating world of gut microbiomes and learn how to assess and maintain a healthy balance within your digestive tract.
We’ll begin by defining the microbiome, exploring its benefits, and discussing factors that impact its composition. Next, we’ll examine various testing methods of “how do I know if my microbiome is healthy”, weighing their pros and cons along with cost considerations.
We’ll then look at signs of an unhealthy microbiome, exploring possible sources and the potential long-term health implications. Finally, we will provide actionable strategies for improving your microbiome health through dietary changes, supplements, and lifestyle habits that promote a thriving gastrointestinal ecosystem.
Embark on this journey towards understanding “how do I know if my microbiome is healthy” so you can take control of your family’s wellness from within.
Table of Contents
- How do I Know if My Microbiome is Healthy
- Lifestyle Choices Impacting Gut Microbiomes
- Diet Considerations for Healthy Gut Bacteria
- Exercise Benefits for Gastrointestinal Health
- Seeking Medical Advice when Necessary
- Conclusion
How do I Know if My Microbiome is Healthy
One way of “How do I know if my microbiome is healthy” is by monitoring the frequency and consistency of your bowel movements. A healthy pattern typically involves pooping between three times a day and three times a week, with stool that is predominantly brown in color, smooth in texture, and passes easily either as one large piece or few smaller pieces. By keeping an eye on these characteristics, you can identify any changes that may indicate poor gut health.
Identifying Healthy Stool Characteristics
A healthy stool should have the following features:
- Brown in color due to bile pigments from the liver.
- Firm but not hard – it should be easy to pass without straining.
- S-shaped or formed into small segments like sausage links.
- Painless during passage with minimal odor.
If you notice significant deviations from these characteristics, such as consistently loose stools or difficulty passing them despite adequate hydration and fiber intake, this could be a sign of an unhealthy gut microbiome.
Recognizing Abnormal Bowel Movement Patterns
In addition to assessing stool quality when looking at “How do I know if my microbiome is healthy”, it’s essential to monitor how often you’re having bowel movements. While individual patterns vary slightly depending on factors like diet and exercise habits, there are some common signs of poor gut health related to bowel movement frequency:
- Constipation: Infrequent bowel movements (less than three per week) accompanied by hard stools may indicate constipation caused by insufficient water intake or lack of dietary fiber. Constipation can be an indicator of imbalances in the gastrointestinal tract or large intestines, potentially signaling poor gut health.
- Diarrhea: Frequent loose stools (more than three times per day) could signal poor gut health due to food allergies, lactose intolerance, or digestive tract infections. Prolonged diarrhea can lead to dehydration and nutrient deficiencies if not addressed promptly.
When it comes to “how do I know if my microbiome is healthy”, one can gain insight by tracking changes in bowel movements. Lifestyle choices, including smoking and taking of drugs, can significantly affect the population of bacteria in one’s intestinal tract.
Lifestyle Choices Impacting Gut Microbiomes
Our daily habits and lifestyle choices play a significant role in “How do I know if my microbiome is healthy”. Behaviors like smoking or consuming certain drugs can detrimentally affect our digestive system’s wellness. By understanding these impacts, we can make informed decisions to improve and maintain good gut health.
Smoking’s Effect on Gut Health
Research has shown that smokers are more likely to experience acid reflux and peptic ulcers compared to non-smokers. This is because smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus causing heartburns or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Additionally, smoking reduces blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, impairing its ability to heal itself from damage caused by harmful substances found in cigarette smoke.
Medications Disrupting Gut Bacteria Balance
Certain medications can disrupt the balance of bacteria within our guts leading to various digestive symptoms like bloating or diarrhea. For example:
- Antibiotics: These drugs are known for killing both bad and good bacteria indiscriminately within our bodies resulting in unhealthy gut flora. It is crucial only take antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow proper dosage instructions.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Regular use of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, can cause damage to the gastrointestinal lining and increase the risk of developing ulcers. It is essential to use these medications responsibly and under a doctor’s guidance.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These medications are commonly prescribed for acid reflux or GERD but may alter gut bacteria composition over time leading to poor gut health. Consult with your healthcare provider if you experience digestive issues while taking PPIs.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by avoiding smoking and using medications responsibly will significantly contribute towards achieving optimal gut health. Before making any alterations to your medication, seek advice from a medical professional.
Diet Considerations for Healthy Gut Bacteria
Your diet plays a significant role in maintaining the health of your gut microbiome. Consuming processed foods high in added sugars can negatively impact your gut bacteria while incorporating collagen-rich foods into your meals helps support better digestion by promoting natural collagen production within the body.
Foods Detrimental to Good Gut Health
Processed and sugary foods are known to be harmful to our gut health. They can lead to an imbalance in our gut bacteria, which may result in various digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Some common culprits include fast food items, artificial sweeteners, fried or fatty foods, caffeinated beverages like coffee and soda, and alcohol consumption.
Collagen-Rich Food Benefits for Digestion
Incorporating collagen-rich foods into your diet can have numerous benefits on overall digestion by supporting natural collagen production within the body. Collagen – a protein located in various parts of the body like skin, bones, and muscles – is essential for keeping up the healthy intestinal wall structure.
Eating more of these types of nutrient-dense ingredients will not only help you achieve better digestive function but also provide additional advantages such as improved skin elasticity or joint pain relief among others.
Some collagen-rich foods to consider adding to your diet include bone broth, fish (especially wild-caught salmon), eggs, leafy greens like spinach and kale, and citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits. In addition to incorporating these collagen-boosting foods into your meals, it’s also essential to maintain a balanced diet that includes plenty of fiber from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
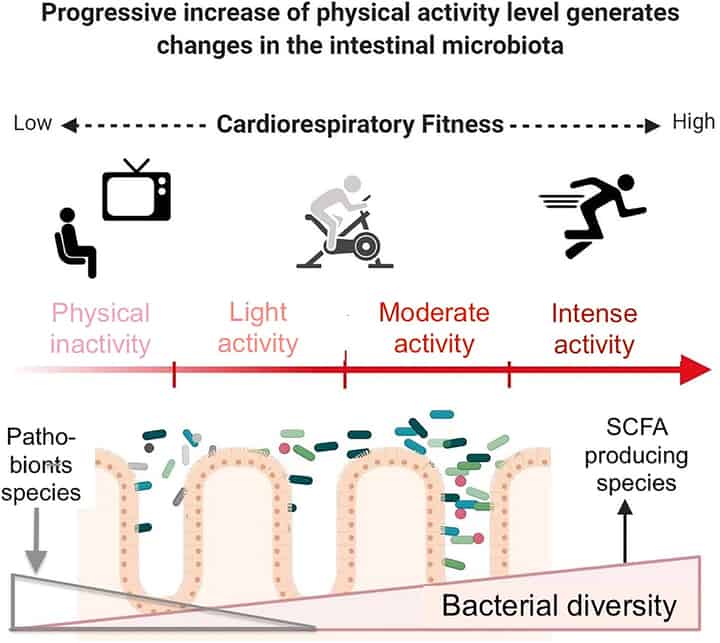
Exercise Benefits for Gastrointestinal Health
Engaging regularly in physical activities aids proper digestion processes, ensuring the optimal functionality of our guts’ microbial communities. Exercise has been proven beneficial for maintaining good gastrointestinal health, which ultimately enhances overall well-being both physically and mentally alike.
Types of Exercise Supporting Healthy Digestion
Different types of exercise can contribute to a healthy gut by promoting blood flow and muscle contractions within the digestive tract. Some effective exercises that support healthy digestion include:
- Aerobic exercises: Activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling help increase heart rate and stimulate intestinal muscles to contract more efficiently.
- Yoga: Yoga poses such as twists and forward bends can gently massage internal organs while improving flexibility and reducing stress levels.
- Pilates: Pilates focuses on strengthening core muscles that play a crucial role in supporting the digestive system’s function.
How Regular Physical Activity Improves Microbial Communities
Maintaining an active lifestyle not only supports proper digestion but also positively impacts our gut microbiomes. Studies have shown that regular exercise can lead to increased diversity among gut bacteria species – considered essential for good gut health.
Moreover, exercise has been found to decrease inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. By engaging in regular physical activity, you can help reduce inflammation levels within your body while promoting a healthier gut environment for optimal digestion.
Exercise is an important factor in maintaining a healthy gastrointestinal system, and regular physical activity can improve microbial communities. Seeking medical advice when necessary is also essential for diagnosing any underlying conditions that may be affecting your gut health.
Seeking Medical Advice when Necessary
While following the recommendations mentioned above can significantly improve your gut health, there may be instances where medical advice becomes necessary. Persistent bloating or abdominal pains despite adhering to these guidelines might indicate an underlying condition that requires further investigation.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Gut Health Concerns
- Persistent symptoms: If you experience ongoing digestive issues such as chronic constipation, diarrhea, or unexplained weight loss even after making lifestyle changes, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
- Sudden onset of severe pain: Severe abdominal pain could signal an acute issue like appendicitis or gallstones and warrants immediate medical attention.
- Blood in stool: The presence of blood in your stool is not considered healthy and should be discussed with a doctor promptly.
- Anemia or fatigue: Chronic fatigue and iron deficiency anemia can sometimes result from poor gut health due to malabsorption of nutrients. Consult with a healthcare provider if you suspect this may be the case for you.
To ensure optimal gut health, prioritizing quality sleep and mindful eating are key components of a healthy lifestyle. Chewing thoroughly and eating at a slow pace allows adequate time for proper nutrient breakdown and absorption within the body, ultimately enhancing overall gut health.
Conclusion
In the end, knowing what signs to look for can help with “How do I know if my microbiome is healthy”. Testing your microbiome regularly, eating a balanced diet rich in probiotics and prebiotics, exercising regularly, reducing stress levels, and avoiding antibiotics when possible are all great strategies for improving the health of your microbiome. Doing these things will ensure that you have an optimal balance of bacteria in your gut.