How to Diversify Your Gut Microbiome for a Healthier Family
Understanding how to diversify your gut microbiome is crucial for maintaining optimal health in today’s modern family. A balanced and varied gut microbiota can be a great asset for general well-being, impacting physical and mental health. In this blog post, we will look into how to diversify your gut microbiome for improved health and well-being.
We will discuss the importance of plant-based foods rich in dietary fiber, which not only promotes gut health but also contribute to the production of short-chain fatty acids with numerous benefits. Additionally, we will delve into polyphenols found in yogurt and their role in supporting intestinal health.
Furthermore, we’ll examine environmental factors such as chronic stress and its impact on gut microbiome diversity. We’ll also emphasize the significance of establishing a healthy infant gut microbiome through diet early on. Lastly, learn how incorporating probiotics into your long-term diet plan can aid in fostering a more diverse microbial species within your digestive system while improving overall health by interacting with polyphenols.
Table of Contents
- Plant-Based Foods for a Diverse Gut Microbiome
- Polyphenols and Yogurt for Intestinal Health
- The Impact of Chronic Stress on Gut Health
- Probiotics’ Role in Promoting Microbiome Diversity
- FAQs in Relation to How to Diversify Your Gut Microbiome
- Conclusion
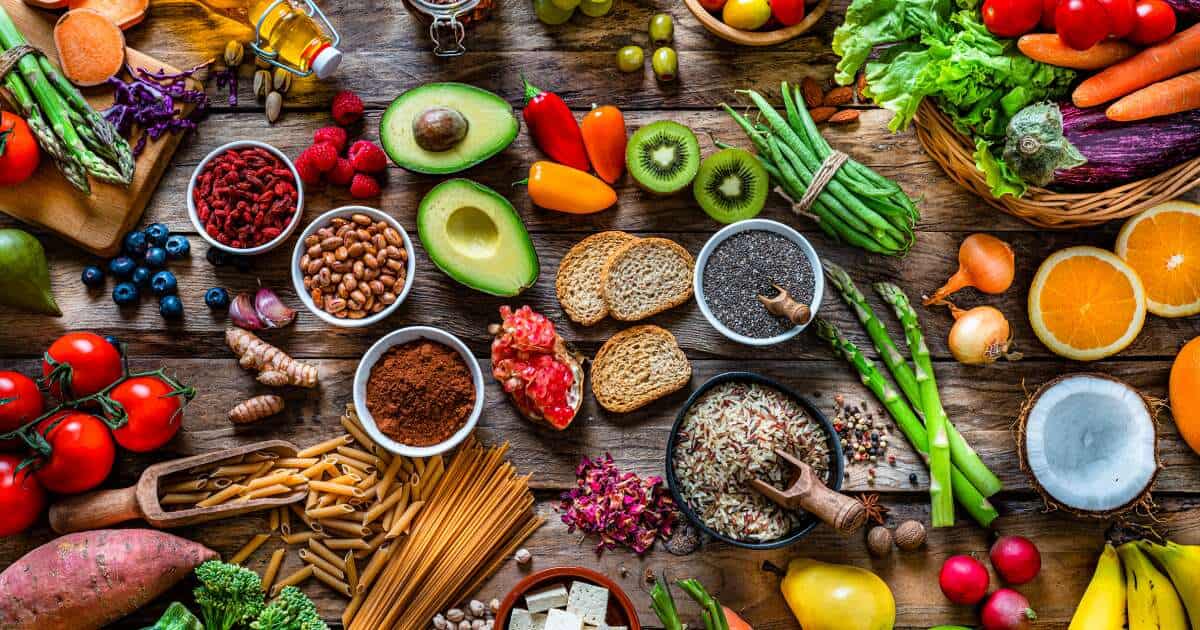
Plant-Based Foods for a Diverse Gut Microbiome
Knowing how to diversify your gut microbiome is important. Consuming a colorful array of vegetables, fruits, legumes, beans, and whole grains daily is essential for diversifying your gut microbiome.
The Importance of Dietary Fiber in Promoting Gut Health
Dietary fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system by providing food for beneficial bacteria residing in our gastrointestinal tract. A study has shown that individuals with higher intakes of dietary fiber have a more diverse microbiome compared to those who consume less fiber. You can eat these for dietary fiber:
- Fruits: Apples, berries, bananas, oranges, pears, etc.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, kale, cucumbers, kidney beans, etc.
- Potatoes– Sweet potatoes, yams, white potatoes, etc.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black-eyed peas.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, barley, oats, wheat, cornmeal, rye, etc.
Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Their Benefits
Gut microbes produce SCFAs such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate when fermenting dietary fiber from whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, etc. These SCFAs have numerous health benefits:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: SCFAs can help reduce inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Gut barrier function: Butyrate is known to improve the integrity of the gut lining, preventing harmful substances from entering our bloodstream.
- Blood sugar regulation: Propionate has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Polyphenols and Yogurt for Intestinal Health
Including foods with polyphenols and yogurt in your diet is essential for sustaining a diverse gut microbiome. Polyphenols, found in many fruits, vegetables, teas, wines, and cocoa, can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress while improving cholesterol levels.
Benefits of Consuming Plain Unsweetened or Flavored Minimal Added Sugar Yogurt
Yogurt is an excellent source of probiotics – live microorganisms that provide numerous health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. These beneficial bacteria aid digestion, boost immunity, and promote overall gut health. When choosing yogurt for yourself or your family members:
- Select plain unsweetened varieties to avoid added sugars.
- If you prefer flavored yogurts with minimal added sugar, look for those sweetened with fruit purees or small amounts of honey.
- Opt for yogurts containing active cultures such as Lactobacillus acidophilus to ensure maximum probiotic benefits.
Polyphenol-Rich Foods: A Powerful Ally for Gut Health
Polyphenols are a diverse group of plant compounds linked to numerous health benefits, including improved digestion and gut health. These powerful antioxidants help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals while also promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Some examples of polyphenol-rich foods include:
- Berries (e.g., blueberries, strawberries, raspberries).
- Leafy greens (e.g., spinach, kale).
- Nuts and seeds (e.g., almonds, walnuts).
- Olives and olive oil.
- Dark chocolate.
- Red wine (in moderation).
The Impact of Chronic Stress on Gut Health
Chronic stress has been linked to various gastrointestinal problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). When under unrelenting tension, our bodies manufacture increased amounts of cortisol, which can cause inflammation and harm the immune system.
To combat these negative effects on your gut health caused by chronic stress:
- Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises regularly.
- Incorporate regular physical activity into your daily routine.
- Prioritize getting adequate sleep each night.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in whole foods that promote healthy digestion and support a diverse range of beneficial bacteria within the gut ecosystem.
Importance of Establishing a Diverse Infant Gut Microbiome Through Diet
A baby’s microbiome begins developing at birth; proper establishment during infancy is crucial for long-term well-being. Introducing whole grains into your child’s diet not only improves their intestinal flora but also reduces inflammation and heart risks for adults alike. Parents should incorporate more plant-based, polyphenol-rich foods such as berries, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, olives, and dark chocolate into their family’s diet.
Here are some tips on how to establish a diverse infant gut microbiome:
- Breastfeed your baby if possible; breast milk contains essential nutrients and beneficial bacteria that help build a healthy gut microbiome in infants.
- When introducing solid foods at around six months, start with whole grains like rice or oatmeal cereals before moving on to fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid giving your child sugary drinks or processed snacks high in salt, which can negatively impact the development of their gut microbiota.
Probiotics’ Role in Promoting Microbiome Diversity
If you want to know how to diversify your gut microbiome, you need to know about probiotics. Probiotics play a crucial role in improving the function of certain gut bacteria and promoting microbiome diversity. Consuming adequate amounts of these living microorganisms may offer numerous advantages for sustaining a balanced gut microbiota.
The Benefits of Incorporating Probiotics into Your Diet
Adding probiotics to your diet can help promote a healthy gut microbiome with many potential benefits. Some key benefits include:
- Improved digestion: Probiotics help break down food particles, making it easier for your body to absorb essential nutrients.
- Better immune function: A balanced gut microbiota supports a strong immune system by preventing harmful pathogens from colonizing the intestinal lining.
- Mental health support: There is growing evidence that suggests a link between gut health and mental well-being. Consuming probiotics may improve mood disorders such as anxiety and depression through their impact on neurotransmitter production.
- Allergy relief: Studies have shown that regular consumption of probiotics may reduce allergy symptoms by modulating the immune response.
How Polyphenols Interact with Gut Bacteria to Improve Overall Health
Polyphenols are naturally occurring compounds in various plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, teas, wines, and cocoa. They possess antioxidant properties that contribute to their numerous health benefits. One such benefit is the ability to interact with gut bacteria and promote microbiome diversity.
Studies have shown that polyphenols from cocoa can increase the amount of Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in humans while reducing Clostridia levels. This suggests a potential role for probiotics in promoting microbiome diversity by enhancing the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppressing harmful ones. To reap these benefits, consider incorporating more polyphenol-rich foods into your diet alongside probiotic supplements or fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha.
FAQs in Relation to How to Diversify Your Gut Microbiome
How do you diversify your gut microbiome?
A diverse microbiome is essential for optimal health and well-being. To foster a diverse gut microbiome, incorporate whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds into your diet. In addition, consider adding probiotic-rich fermented foods such as yogurt or kimchi to your diet.
What are three things you can do to improve your gut microbiome?
- Consume a selection of fermented edibles, like sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, and yogurt, to introduce helpful microorganisms into your gut microbiota.
- Take probiotic supplements that contain live cultures to supplement the beneficial bacteria in your digestive system.
- Reduce sugar intake and processed food consumption as these can damage the balance of good bacteria in your gut microbiome leading to an unhealthy state over time.
What is the best diet for microbiome diversity?
The best diet for microbiome diversity emphasizes a variety of whole, unprocessed foods from all food groups. To achieve a balanced diet, consuming lean proteins such as fish or poultry, healthy fats like olive oil and nuts, complex carbohydrates like whole grains, and plenty of fruits and vegetables is recommended.
Eating fermented foods can also help increase microbial diversity in the gut. Additionally, limiting processed foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates will promote better overall health by providing essential nutrients to support a diverse microbiota population.
Conclusion
The modern family is responsible for their own health and well-being. Investing in a balanced gut microbiome can be beneficial for overall health, but it requires commitment and hard work.
Eating nutrient-rich foods, managing stress levels, practicing good sleep hygiene, and considering environmental factors are all key components of cultivating a healthy gut microbiome. With these tips in mind, you can take steps toward improving your family’s physical and mental health now.
Discover how to diversify your gut microbiome and achieve a healthier lifestyle with Smart Living Now. Our no-nonsense resources provide you with the tools needed for independent wellness success.