Exploring What Bacteria Do in a Healthy Gut Microbiome
What do bacteria do in a healthy gut microbiome? Research into the importance of these minuscule life forms in human health has been ongoing, with scientists seeking to understand their purpose. We’ll investigate the part that bacteria play in setting up and keeping our vulnerable framework, just as their effect on weight.
Furthermore, we’ll discuss probiotics – beneficial microorganisms that help maintain a balanced gut microbiome – along with food sources containing them and their associated benefits. Finally, you’ll learn about practical guidelines for maintaining good gut health, such as adopting fiber-rich diets for better digestion, avoiding processed foods & refined sugars, managing stress effectively through relaxation techniques, and using antibiotics. By understanding what do bacteria do in a healthy gut microbiome and implementing these recommendations into your daily life, you can take steps towards improved overall wellness for yourself and your family.
Table of Contents
- The Role of Bacteria in a Healthy Gut Microbiome
- Probiotics for Maintaining a Balanced Gut Microbiome
- Guidelines to Maintain Good Gastrointestinal Health
- FAQs in Relation to What Do Bacteria Do in a Healthy Gut Microbiome
- Conclusion
The Role of Bacteria in a Healthy Gut Microbiome
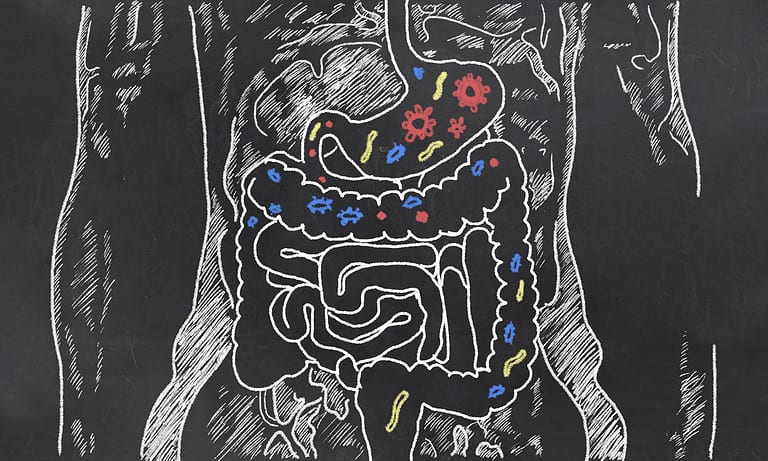
A healthy gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms and gut microbes such as bacteria, fungi, yeast, and viruses living inside our bodies. They play a crucial role in maintaining human health. It is essential for the development and maintenance of the immune system and has a significant impact on obesity development and progression.
Development and Maintenance of the Immune System
Bacteria in our gut have a symbiotic relationship with our body. They help break down food into nutrients that can be easily absorbed by the intestines while also producing essential vitamins like vitamin K and certain B vitamins. This process not only aids digestion but also supports the proper functioning of the immune system.
Moreover, these beneficial bacteria act as a barrier against harmful pathogens entering through the gastrointestinal tract by competing for resources or secreting substances that inhibit their growth. The balance between helpful and detrimental bacteria in the intestinal microbiome can be kept at its best by this approach.
- Beneficial bacterial strains: Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum,
- Harmful bacterial strains: Escherichia coli O157:H7, Clostridium difficile.
Impact on Obesity Development
An imbalance in gut microbiota composition has been linked to various health issues, including obesity – one major public concern worldwide today due to its increasing prevalence among both adults and children alike across nations. Research suggests that the gut microbiome may influence energy metabolism, inflammation, and insulin resistance – all factors contributing to obesity development.
Studies suggest that individuals with a greater abundance of firmicutes in their gut microbiome may be more prone to extracting additional calories from food, potentially leading to weight gain if not managed correctly.
Probiotics for Maintaining a Balanced Gut Microbiome
So what do bacteria do in a healthy gut microbiome? A healthy gut microbiome and microbial diversity are essential for overall well-being, and one way to achieve this balance is by incorporating probiotics into your diet.  Source
Source
Probiotics are living organisms that can have advantageous impacts on human well-being when taken in suitable amounts. They can be found in food items, dietary supplements, or drugs.
Food sources containing probiotics
The most common and easily accessible source of probiotics comes from fermented foods. These foods undergo a process where bacteria break down sugars and starches, producing lactic acid, which helps preserve the food while providing numerous health benefits. Some popular examples of probiotic-rich foods include:
- Yogurt.
- Kefir.
- Kombucha tea.
- Sauerkraut.
- Kimchi.
Benefits associated with consuming probiotics
Including probiotic-laden foods in your meals may bring a variety of health advantages. Some potential advantages include:
- Prevention or reduction of diarrhea episodes: Probiotics have been shown to help prevent or reduce the duration and severity of diarrhea during irritable bowel syndrome caused by antibiotic treatment or infections.
- Necrotizing enterocolitis prevention: This severe intestinal condition affects premature infants, and studies have suggested that probiotic supplementation may help reduce its incidence.
- Acute upper respiratory tract infections reduction: Research has indicated that consuming probiotics may lead to fewer acute upper respiratory tract infections, particularly in children. One study showed a reduced rate of such infections when children consumed milk containing Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, a specific strain of bacteria often used as a probiotic.
- Pulmonary exacerbations management for cystic fibrosis patients: Children suffering from cystic fibrosis may benefit from regular consumption of certain strains of probiotics which could potentially lower their risk for pulmonary exacerbations.
Guidelines to Maintain Good Gastrointestinal Health
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall well-being. While symptoms indicating an unhealthy gut may vary among individuals, there are general guidelines you can follow to ensure good gastrointestinal health.
Fiber-rich diets for better digestion
A diet rich in fiber promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria and supports regular bowel movements. Fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds should be consumed to promote healthy digestion and balance the gut microbiome.
Avoiding processed foods & refined sugars
Processed foods and refined sugars can negatively impact your gut health by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria. To keep your gut microbiome balanced, it’s important to limit or avoid consuming these types of food products.
Managing stress effectively through relaxation techniques
Elevated cortisol levels due to chronic stress can have adverse effects on your gastrointestinal system. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation into your daily routine can help manage stress more effectively while supporting a healthier gut environment.
Judicious use of antibiotics
While antibiotics can be life-saving, their overuse or misuse can disrupt the balance of your gut microbiome. It’s essential to use antibiotics only when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow the recommended dosage instructions. If you need to take antibiotics, consider discussing probiotic supplementation with your doctor as a way to support the recovery of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
FAQs in Relation to What Do Bacteria Do in a Healthy Gut Microbiome
What do bacteria do in a healthy gut microbiome?
Bacteria are essential for the well-being of our intestinal ecosystems, aiding in digestion and supplying vitamins while warding off dangerous microorganisms. Bacteria are indispensable for breaking down food, obtaining nutrients, producing vitamins, modulating hormones, shielding from dangerous microorganisms, and aiding the immune system. Moreover, bacteria are necessary for the digestion and assimilation of macronutrients such as carbohydrates and fats.
What are the functions of gut bacteria?
What do bacteria do in a healthy gut microbiome? Gut bacteria play a vital role in human health. They aid digestion and nutrient absorption, synthesize vitamins and other essential compounds, protect against harmful pathogens, regulate the immune system, produce hormones that affect appetite and metabolism, influence mental health by producing neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, modulate inflammation levels throughout the body to reduce risk of chronic disease development, like, inflammatory bowel disease.
Conclusion
Understanding what do bacteria do in a healthy gut microbiome can help you make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle and when to seek medical advice. By taking proactive steps to improve your gut health through probiotic foods or supplements, prebiotics that feeds beneficial bacteria, reducing stress levels, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet rich in fiber – you can ensure optimal functioning of your digestive system and support the important work gut microbes do in a healthy gut microbiome.
Discover how to prioritize your gut health and live a healthier, more independent lifestyle with Smart Living Now. Our resources provide practical solutions for modern families seeking to nourish their microbiome and optimize their overall well-being.