Can Gut Microbiome Be Restored: Guide to Optimal Gut Health
Can gut microbiome be restored? The answer lies in understanding what gut microbiota is and how to restore healthy gut flora with good bacteria.
Rebalancing the microbiome in your gut can potentially provide many advantages such as improved digestion, greater protection from disease, and clearer cognitive functioning. However, there are also certain risks involved when attempting to restore gut microbiome diversity which you should take into consideration before modifying your diet.
In this article, we will explore how can gut microbiome be restored safely — with some actionable steps you can take today toward restoring the health of your gut microbiota.
Table of Contents
What is a Gut Microbiome?
The microorganisms inhabiting our intestines form the gut microbiome. The bacteria, fungi, and viruses that live in this system all play a role in maintaining optimal gut health. These microscopic creatures are essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune system functioning.
The gut microbiome consists of beneficial gut bacteria and bad bacteria. This diverse community helps us break down food, regulate hormones, generate vitamins like B12, protect against disease-causing organisms, facilitate detox, and regulate inflammation levels throughout the body. It can even stop the overgrowth of harmful gut bacteria or yeast in the intestines while influencing mood through the production of the neurotransmitter serotonin.
Good Bacteria and Gut Health
Good bacteria are live microorganisms that help keep our gut microbiome balanced and healthy by maintaining an optimal balance between “good” and “bad” bacteria. The good guys prevent the bad ones from taking over your digestive system while promoting overall well-being. Plus, they help break down food more efficiently so you get the most nutrients out of it.
Benefits of Good Bacteria
Having enough good bacteria in your gut has many advantages for both physical and mental health. It helps improve digestion by breaking down hard-to-digest foods into smaller molecules that are easier to absorb so get more nutrition out of what you eat.
Good bacteria also play an important role in immunity by acting as a first-line defense against harmful pathogens entering the body through the digestive tract.
They also reduce inflammation throughout the body which can lead to improved moods, better sleep quality, reduced stress levels, and even clearer skin.
Finally, these friendly microbes aid nutrient absorption so you don’t miss out on any essential vitamins or minerals needed for optimal functioning.
How Antibiotics Can Damage Your Gut
Antibiotics are medicines that fight bacterial infections and are often prescribed when a person has bronchitis or strep throat. They work by killing the bacteria causing the infection or preventing them from multiplying and spreading further throughout your body.
However, antibiotics can also kill beneficial bacteria in your gut microbiome, which is why it’s important to restore your gut flora after taking antibiotics.
How Antibiotics Affect Gut Health
When you take antibiotics, it doesn’t just target bad bacteria. It targets all types of bacteria including good ones that help keep our bodies functioning properly and protect us from other illnesses. This disruption of the delicate balance between good and bad microbes can cause digestive issues like diarrhea, nausea, bloating, and constipation as well as other side effects like headaches or fatigue.
In some cases, this disruption may even lead to more serious conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
Long-Term Effects of Damaged Gut Health
Chronic Inflammation
Damaged gut health can cause chronic inflammation. When this happens, it triggers a cascade of events that leads to fatigue, joint pain, skin issues like eczema and psoriasis, digestive problems such as irritable bowel syndrome, and even depression and anxiety.
Weakened Immunity
An unhealthy gut microbiome also weakens your immune system because it decreases your ability to absorb essential vitamins and minerals needed for the proper functioning of your cells – including those responsible for fighting off infections or disease-causing organisms. This means you are more likely to catch colds or other illnesses.
Risk of Later-Onset Diseases
Research has found that an unbalanced microbiota increases the risk for later-onset diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s. These diseases have been linked to poor dietary habits that affect the composition of bacteria in our gut.
Benefits of a Healthy Microbiome
If your microbial diversity is poor and unbalanced — meaning you have more harmful bacteria than beneficial bacteria — then you should make an effort to restore the health of your gut microbiome.
Improved digestion is one of the most significant advantages of restoring the gut microbiome. The beneficial bacteria that inhabit a balanced gut microbiome can help in the digestion of food, less bloating and gas, absorption of nutrients, fewer episodes of diarrhea or constipation, and protection against potentially dangerous pathogens.
An enhanced immune system is another major benefit of restoring the gut microbiome. Good bacteria contribute to our body’s natural defense and help fight off invading pathogens to keep our bodies strong and resilient. Studies have indicated that individuals with a balanced microbiome may suffer fewer colds or other ailments.
Finally, replenishing the microbial inhabitants of your digestive system may help lower the odds of developing certain long-term ailments like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer due to its ability to control inflammation. By keeping inflammation in check, you can improve your health outcomes while reducing your risk for these conditions.
But can gut microbiome be restored?
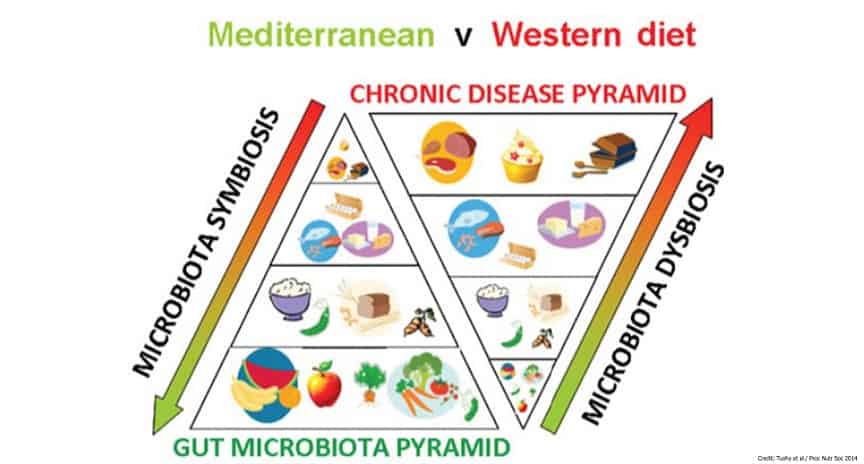
(Source)
How Can Gut Microbiome Be Restored?
Antibiotics kill good bacteria, and if you’re taking too many pills, it could lead to damaged gut health. When this happens, can gut microbiome be restored?
To restore gut health, you have to make dietary changes and lifestyle changes.
Diet and Nutrition Strategies for Restoring Gut Flora
Diet plays an essential role in restoring beneficial gut bacteria in the gut flora. Foods like prebiotics and probiotics contain good bacteria that can help repopulate the intestines with healthy microbes.
Probiotics can be found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi while prebiotic-rich foods include onions, garlic, bananas, and oats. Prebiotics and probiotics feed the good bacteria already present in the intestines, which helps restore the right balance in a healthy gut microbiome.
Supplements to Restore Gut Flora
Supplements are another way to restore the balance of your gut microbes. Probiotic supplements contain various strains of beneficial bacteria which may aid in digestion when taken daily. Prebiotic fiber supplements such as psyllium husk powder may also be helpful if you’re having difficulty getting enough prebiotics from food sources alone.
Beat Stress for a Healthier Digestive Tract
Besides adjusting dietary habits, lifestyle changes can help restore your good gut microbes. Reducing stress levels has been linked with improved microbial diversity while regular exercise has been shown to increase beneficial bacterial populations within the intestine – both helping towards restoring balance back into your gut microbes.
Avoid Antibiotics
Lastly, avoid taking antibiotics unless absolutely necessary. Antibiotics are known to disrupt microbial populations, leading to imbalances that require restoration.
Potential Risks of Restoring Gut Microbiome
Despite the potential benefits of restoring your gut health, there are risks involved in any type of microbiome restoration program.
Consuming unfamiliar ingredients could lead to allergic reactions so it is important to be aware of what you are eating. If you have a dairy allergy, be sure that lactose is not present in the probiotics product you are consuming. Always read the label and consult your doctor before starting a gut microbiome diet.
The introduction of too much good bacteria into the body can also lead to the overgrowth of bad bacteria in the intestines. For instance, lactobacillus acidophilus which is known for promoting healthy digestion may cause infections if consumed in excessive amounts — leading to bloating and cramping pains.
Therefore, you should only consume probiotic-rich products under medical supervision and with gradual increases in dosage until your body becomes accustomed to them.
Conclusion
How can gut microbiome be restored and is it safe?
Rebuilding the intestinal microbiota can be an excellent approach to promoting gut health and well-being. With proper research and guidance from healthcare professionals, families can make informed decisions about restoring their gut microbiome in order to reap its many benefits.
Smart Living Now offers comprehensive resources to help you restore your gut microbiome and achieve a healthier lifestyle. Learn how to take control of your health today with our no-fluff solutions!





