Does Gut Microbiome Affect the Brain? Key Insights
Does gut microbiome affect the brain? This captivating query has been a focus of scientific investigation in recent times as we persist to understand the intricate links between our gut and brain. In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of gut microbes and their potential impact on various aspects of brain functioning.
We’ll begin by exploring what exactly constitutes the gut microbiome, its components, and how a healthy balance contributes to overall well-being. Then, we will discuss the ways in which these tiny microorganisms can influence neurotransmitter production, inflammation regulation, stress response mechanisms, and cognitive function. Armed with this knowledge about how does gut microbiome affect the brain, you’ll be eager to learn strategies for improving your own gut health.
Table of Contents
- The Gut-Brain Connection: Does Gut Microbiome Affect the Brain?
- Pathways of Communication Between Gut Microbes and The Brain
- Animal Studies Exploring Gut-Brain Interactions
- Probiotics for Mental Health
- Long-term Antibiotic Use & Cognitive Performance
- Yogurt’s Impact on Emotion-Processing Centers
- Conclusion
The Gut-Brain Connection: Does Gut Microbiome Affect the Brain?
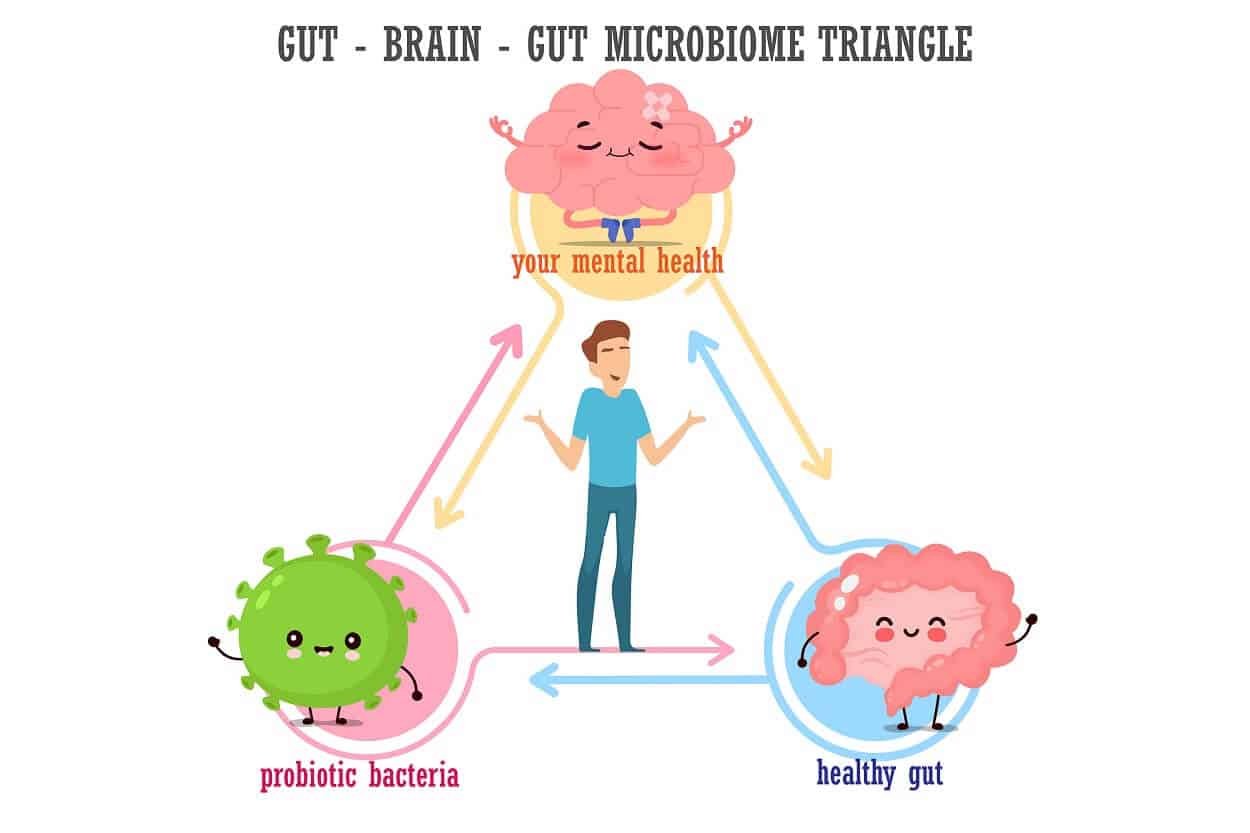
Research suggests that gut microbes may influence the brain and behavior across various animals by communicating with the brain through numerous pathways. Animal studies have provided intriguing insights into these interactions, showing that interventions such as probiotics, dietary changes, and meditation can help alter our microbiota.
Pathways of Communication Between Gut Microbes and The Brain
How does gut microbiome affect the brain? Gut bacteria communicate with the brain via several mechanisms including:
- Vagus nerve signaling: This is a direct line of communication between gut bacteria and neurons in the central nervous system (CNS).
- Neurotransmitter production: Certain gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin or dopamine which are crucial for mood regulation.
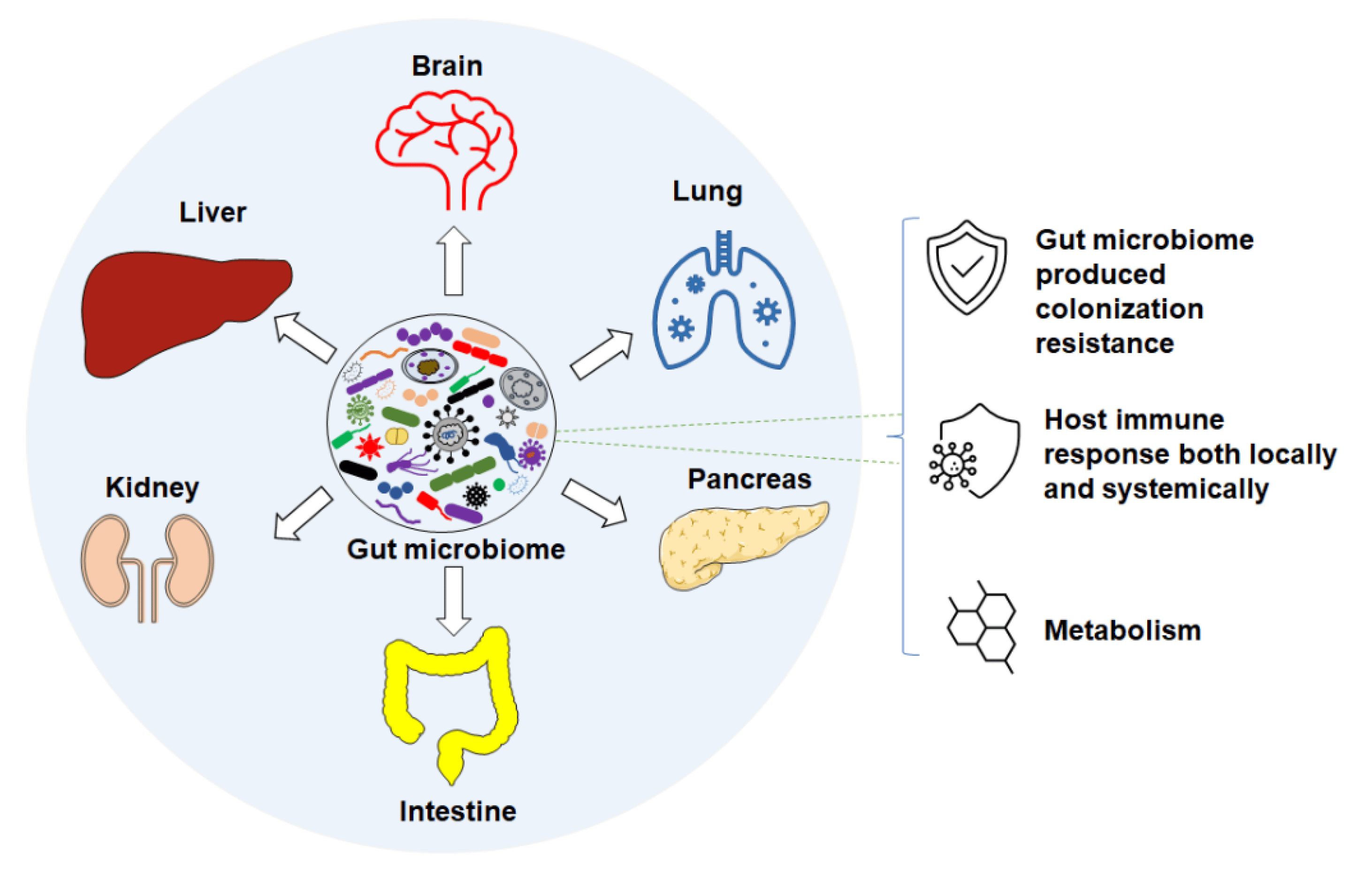
- Immune system modulation: Gut microbes can interact with immune cells to produce inflammatory molecules affecting CNS function.
- Metabolite production: Some bacterial metabolites can cross the blood-brain barrier influencing neuronal activity directly or indirectly.
Animal Studies Exploring Gut-Brain Interactions
Recent studies have explored the potential impacts of gut bacteria on brain function and behavior in animals. For example:
- Germ-free mice: Mice raised without any exposure to microbes showed increased stress responses, anxiety-like behaviors, and impaired cognitive function compared to those with a normal gut microbiome.
- Probiotic treatment in rodents: Administration of specific probiotic strains led to reduced anxiety- and depression-like behaviors as well as improved learning abilities in rats.
These findings demonstrate the need to keep a balanced microbiome for optimal health. Given the profound link when it comes to “Does gut microbiome affect the brain”, it is evident that proper maintenance of the digestive system can have a considerable effect on mental well-being.
Probiotics for Mental Health
In recent years, researchers have been exploring how prebiotics and probiotics might be used to treat mental health conditions. One study found that a multispecies probiotic improved emotional processing and cognition in people with mild to moderate depression.
Prebiotics vs. Probiotics
Prebiotic fibers, which are naturally present in foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and whole grains, serve as food for gut microbes. These substances help stimulate the growth of healthy gut bacteria populations while suppressing harmful ones.
Probiotic supplements or foods, such as yogurt or fermented vegetables like sauerkraut or kimchi contain live microorganisms that can improve our gut microbiome balance when consumed regularly.
A Study on Multispecies Probiotic Improving Emotional Processing
In a fascinating 2016 study published in Brain Behavior & Immunity, participants with mild-to-moderate depression were given either a placebo or a daily dose of an eight-strain multispecies probiotic supplement for four weeks. The results showed significant improvements in cognitive reactivity to sad moods among those who received the probiotics compared to those who took placebos.
These findings suggest that probiotics may have the potential to improve mental health by modulating emotional processing and cognition.
By consuming foods rich in prebiotics and probiotic or taking supplements when necessary, we can support a healthy balance of gut bacteria, ultimately promoting better mental health. However, more research is needed to fully understand how these beneficial bacteria can be used as a treatment for various mental health conditions.
Long-term Antibiotic Use & Cognitive Performance
In recent years, there has been growing concern about the potential negative effects of long-term antibiotic use on our overall health. One area that has received particular attention is the impact of antibiotics on cognitive performance.
Studies have demonstrated that extended antibiotic use can lead to poorer cognitive performance on tests, compared to those without such exposure. This finding highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy balance within our gut flora for overall well-being.
Effects of Long-term Antibiotic Use on Cognition
A study published in Nature Communications found a correlation between long-term antibiotic use and decreased cognitive function in mice. The researchers discovered that prolonged exposure to antibiotics led to alterations in gut bacteria, which subsequently affected brain function and behavior.
- The study showed reduced spatial memory abilities in mice treated with antibiotics.
- There was also an increase in anxiety-like behaviors among these animals.
- The changes were attributed to alterations in specific types of gut microbes and their metabolites, which are known to influence brain chemistry and neurotransmitter production.
This research raises concerns about how similar changes might occur in humans after long-term antibiotic treatment. This research underscores the necessity for further exploration into this connection so as to more readily comprehend its effects on human thinking and psychological well-being.
Importance of Balanced Gut Flora
For optimal health, it is necessary to maintain a healthy balance of gut flora. A diverse population of beneficial bacteria helps:
- Promote proper immune system functioning.
- Regulate inflammation.
- Synthesize essential vitamins and nutrients.
- Support healthy brain function.
In light of the potential negative effects of long-term antibiotic use on cognitive performance, it is crucial to prioritize a balanced gut microbiome. This can be achieved through various means such as consuming probiotics and prebiotics, eating a diverse diet rich in fiber, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic treatments whenever possible.
Yogurt’s Impact on Emotion-Processing Centers
The consumption of yogurt, which is rich in live bacterial cultures, has been shown to have a significant impact on the emotion processing centers within the brains of healthy women who do not exhibit psychiatric symptoms. This intriguing finding suggests that incorporating foods rich in beneficial bacteria into one’s diet may offer potential benefits for mental health and overall well-being.
Live Bacterial Cultures in Yogurt Affecting Emotion Processing Centers
A study conducted by researchers at UCLA discovered that women who regularly consumed yogurt containing probiotics – specifically, gut microbes like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium – exhibited changes in brain function when compared to those who did not consume such products. The study found that these changes were particularly noticeable within regions responsible for emotion processing and cognition.
This fascinating discovery highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced gut microbiome through dietary choices as it can directly influence our emotional well-being. As we continue to learn more about how gut microbes interact with our brains, it becomes increasingly clear that consuming foods high in beneficial bacteria could play an essential role in promoting optimal mental health.
Incorporating Foods Rich in Beneficial Bacteria
Beyond yogurt, there are several other food options available for individuals looking to incorporate more beneficial bacteria into their diets. Some examples include:
- Kefir: A fermented milk drink similar to yogurt but with a thinner consistency; kefir contains multiple strains of good bacteria and yeast.
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage packed with probiotics; opt for unpasteurized versions to ensure the presence of live bacteria.
- Kimchi: A Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, typically cabbage and radish; it contains a variety of probiotics as well as vitamins and minerals.
- Miso: A Japanese seasoning produced by fermenting soybeans with salt and koji (a type of fungus); miso is rich in beneficial bacteria, particularly Lactobacillus strains.
Incorporating these foods into your daily meals can help support a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn may have positive effects on your brain function and emotional health. It is essential to focus on dietary selections that can sustain a healthy gut microbiome for overall well-being, as studies continue to reveal more regarding the intricate connection between our intestinal microbes and psychological health.
Conclusion
To answer “Does gut microbiome affect the brain?”, evidence suggests that the gut microbiome can significantly influence brain functioning. Studies suggest that incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your diet can promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria, ultimately promoting better mental health. When it comes to “Does gut microbiome affect the brain”, maintaining a balanced gut microbiome through dietary choices can positively influence overall mental health.