How Important is the Gut Microbiome for a Healthy Family?
Understanding how important is the gut microbiome to our overall health has become a significant area of research in recent years. The gut microbiome, consisting of trillions of microbes that are integral to various aspects such as digestion and immune system regulation, has been identified as a critical factor in overall health.
In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of gut microbiota by discussing its composition and how important is the gut microbiome in maintaining optimal health. We’ll also explore practical ways to support healthy gut microbiota through diet, exercise, and stress management.
Furthermore, we’ll examine potential benefits associated with nurturing a healthy gut microbiome such as improved digestive health and reduced risk of chronic diseases. Conversely, we will discuss potential risks that may arise from an unhealthy gut ecosystem like weakened immune system functioning.
Armed with this understanding of how important is the gut microbiome for your family’s well-being, you can make educated decisions about lifestyle choices that foster better overall health and autonomy.
Table of Contents
- Health and Well-being: How Important Is the Gut Microbiome
- Energy Harvesting and Digestion
- Immune System Support
- Influence on Food Cravings
- Diet’s Impact on Gut Microbiota Composition
- Links Between Gut Microbiome Imbalance & Diseases
- Probiotics & Prebiotics for Cognitive Function Improvement
- Gut Microbiome’s Connection to Psychological Disorders
- Conclusion
Health and Well-being: How Important Is the Gut Microbiome
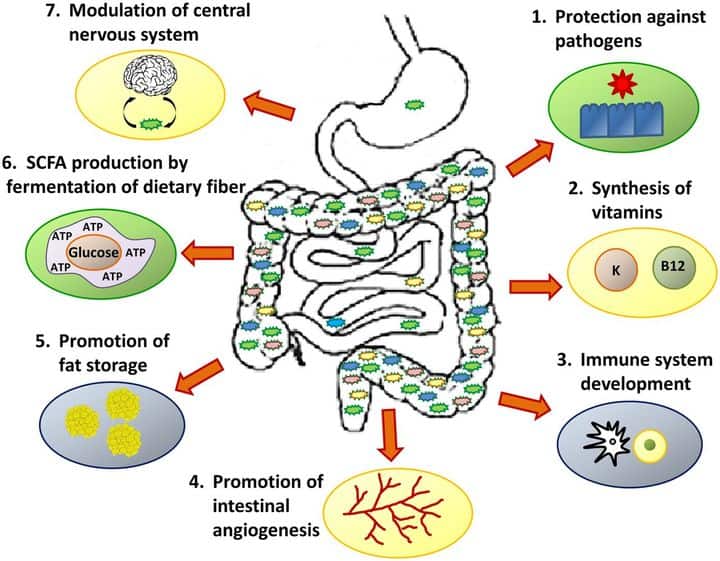
The gut microbiome, consisting of trillions of microbes residing in the human digestive tract, contributes to various physiological functions such as energy harvesting, digestion, immune system, and even influences food cravings and feelings of satiety. An imbalance or disruption in this complex ecosystem can lead to several health issues.
Energy Harvesting and Digestion
One aspect of how important is the gut microbiome is its role in breaking down dietary fibers, which our bodies cannot digest on their own. These beneficial bacteria ferment the fiber into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), providing an essential energy source for colon cells while also aiding overall digestion.
Immune System Support
Another aspect of how important is the gut microbiome Is its part in maintaining a strong immune system. The presence of certain beneficial microbes helps regulate inflammation, protecting us from harmful pathogens while preventing autoimmune diseases caused by immune dysregulation.
Influence on Food Cravings
- Gut bacteria: Some studies suggest that specific types of gut bacteria may influence our food preferences by releasing signaling molecules that affect appetite regulation within the brain – potentially leading to cravings for unhealthy foods when there is lower gut microbiome diversity.
- Satiety hormones: A balanced microbial community can help modulate levels of hormones like leptin and ghrelin – key players involved with hunger signals sent between the stomach and brain – ultimately impacting our feelings of fullness and satiety.
Knowing how important is the gut microbiome for sustaining good health, it’s essential to comprehend how diet affects its makeup. By consuming fiber-rich diets and fermented foods, we can promote beneficial bacteria within our gut microbiota for improved health outcomes.
Diet’s Impact on Gut Microbiota Composition
Your diet plays a significant role in shaping the composition of your gut microbiome. The foods you consume can either promote the growth of beneficial bacteria or contribute to an imbalance, known as gut dysbiosis. By understanding how different dietary patterns affect your gut microbiota composition, you can make smarter choices for a healthier and more balanced gut.
Fiber-rich diets for a healthy gut
A diet high in fiber is essential for maintaining good gut health because it provides nourishment for beneficial microbes. Foods rich in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Consuming these foods helps increase microbial diversity within the gastrointestinal tract while also supporting intestinal barrier function.
Fermented foods promoting beneficial bacteria
Fermented foods are a natural source of probiotics, which help to maintain the balance of gut bacteria and promote overall health. These foods contain live microorganisms that can improve your gut microbiota composition by introducing beneficial microbes into your system. Some popular fermented foods include yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
Adding these fiber-packed, fermented foods to your diet could have a considerable effect on the makeup of your gut microbiome, aiding digestion, immune system functioning, and general health. Before making any significant changes to your diet or taking supplements for conditions such as IBS, Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Links Between Gut Microbiome Imbalance & Diseases
Research has established links between specific microbial compositions across demographics and diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic kidney disease(CKD), Alzheimer’s disease(Parkinson’s Disease) associated with dysbiosis – an imbalance between harmful and helpful microorganisms affecting mucosa-associated microbiota.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Studies have shown that patients with IBD often exhibit microbiota dysbiosis, leading to a lower gut microbiome diversity compared to healthy individuals.
This disruption in the gut ecosystem can contribute to immune dysregulation, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and increased susceptibility to infections. Restoring a balanced gut microbiota composition through dietary interventions or probiotic supplementation may help alleviate symptoms and improve the overall quality of life for those suffering from IBD.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a common metabolic disorder where excess fat accumulates in the liver without significant alcohol consumption. Research suggests that an altered gut microbiota composition may play an important role in NAFLD development by promoting inflammation, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism abnormalities.
A diet low in fiber or high in saturated fats can lead to gut dysbiosis, further exacerbating NAFLD progression. Implementing dietary changes and incorporating prebiotics or probiotics may help improve liver function by promoting a healthier gut microbiome.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic kidney disease is a progressive loss of kidney function over time, often resulting from diabetes, hypertension, or other underlying conditions. Emerging evidence suggests that alterations in the gut microbiota composition can contribute to CKD development and progression through increased production of uremic toxins and inflammation.
It is evident that a discrepancy in gut microbiome equilibrium may result in grave consequences for our well-being. Therefore, it is important to understand how probiotics and prebiotics may be used to improve cognitive function.
Probiotics & Prebiotics for Cognitive Function Improvement
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system involving neural, hormonal, and immunological pathways that contribute to mental disorders such as anxiety. Exploring potential avenues to enhance cognitive well-being, researchers are looking into the association between gut microbiota and brain function via probiotics and prebiotics.
Probiotics and prebiotics for mental health
- Probiotics: These live microorganisms found in fermented foods or supplements can help restore balance within the gut microbiome by promoting beneficial microbes’ growth. Studies have shown potential benefits of probiotics in improving cognitive function in patients suffering from Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s diseases.
- Prebiotics: Non-digestible food components like dietary fiber serve as fuel for beneficial bacteria residing in our guts. A diet rich in prebiotic fibers can support overall gut health while potentially enhancing mood regulation.
Fecal transplantation as a treatment option
Interventions involving fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) have shown promising results in treating certain conditions related to gut dysbiosis. FMT involves transferring healthy donor feces into the patient’s gastrointestinal tract, which can help restore balance within their gut microbiome.
The potential for probiotics and prebiotics to revolutionize mental health treatments by improving cognitive functioning is an exciting area of exploration. As such, it’s important to explore how the gut microbiome may be connected with psychological disorders like major depressive disorder (MDD) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Gut Microbiome’s Connection to Psychological Disorders
Recent studies have uncovered fascinating connections between the gut microbiome and psychological disorders. The gut microbiota, an intricate microbial community in our digestive tract that is essential for human health, has been linked to certain psychological disorders like MDD and ASD. The gut microbiota can become imbalanced, which has been linked to the development of mental health issues such as MDD and ASD.
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Research has shown that individuals with MDD often exhibit increased proportions of certain bacterial species like Prevotella and Klebsiella. These altered gut microbiota compositions may influence brain function through what is referred to as the “gut-brain axis,” which involves bidirectional communication between the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system.
- Prevotella: An increase in Prevotella species has been associated with higher levels of inflammation, which could potentially exacerbate symptoms of depression.
- Klebsiella: Elevated levels of Klebsiella bacteria have been linked to increased production of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), endotoxins that can trigger systemic inflammation and negatively impact mood regulation.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
The relationship between gut microbes and ASD is another area under investigation by researchers. Studies suggest that children with ASD tend to have lower gut microbiome diversity, an imbalance in beneficial versus harmful bacteria, and higher levels of certain bacterial species. These factors may affect the development or severity of ASD symptoms by influencing immune system function, neurotransmitter production, and other physiological processes.
In light of these findings, it’s important for researchers to continue exploring how interventions targeting gut microbiota composition might help alleviate psychological disorders like MDD and ASD. Potential strategies include dietary modifications, probiotic supplementation, prebiotic intake, or even fecal transplantation as a means to restore a healthy balance within our gut microbes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, taking steps to support a healthy gut microbiome can help improve digestion, immunity, moods, and more. But, it’s also crucial to be conscious of any potential hazards linked with an unbalanced or weak gut microbiome so you can take the necessary action if required. By understanding how important is the gut microbiome for your family’s health and well-being, you’ll be able to make informed decisions about what strategies are best for supporting their optimal wellness.