How to Feed Your Gut Microbiome: A Family Guide
Knowing how to feed your gut microbiome is key to keeping a healthy equilibrium of helpful microorganisms and advancing general health. The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in digestion, immune system function, and mental health. We will explore various strategies on how to feed your gut microbiome effectively by embracing plant-based foods rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
We’ll also discuss the importance of avoiding highly processed foods that can negatively impact our microbial community. Lastly, you’ll learn about incorporating fermented foods into your diet as they are packed with live bacteria that support good gut health. By following these guidelines on how to feed your gut microbiome, you can help create an optimal environment for your gut flora to thrive.
Table of Contents
- Embrace Plant-Based Foods for Gut Health
- Avoid Highly Processed Foods
- Incorporate Fermented Foods into Your Diet
- FAQs in Relation to How to Feed Your Gut Microbiome
- Conclusion
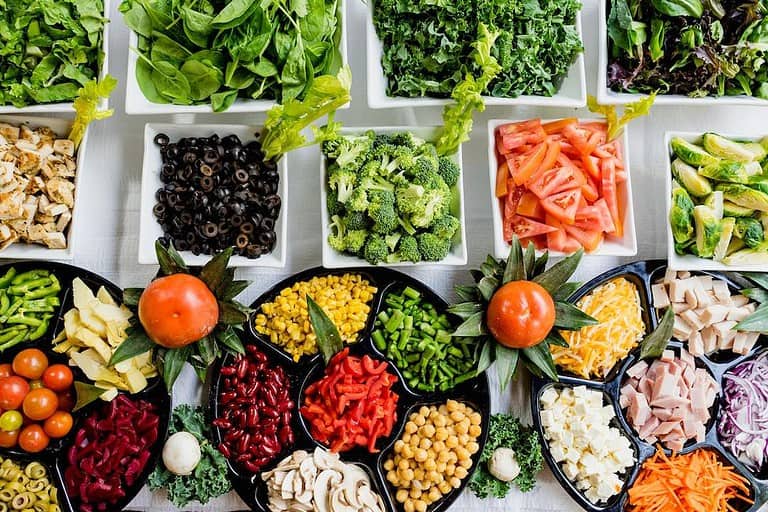
Embrace Plant-Based Foods for Gut Health
Consuming a variety of plant-based foods is essential to promote a diverse and healthy gut microbiota. Include roughly 30 different plant-based sources in your weekly diet, like vegetables, legumes (beans), fruits, herbs, spices, and nuts. These provide soluble fiber that helps balance microbial populations while promoting regular bowel movements.
Incorporate various vegetables in your daily meals
Consuming a range of nutritious veggies not only furnishes essential vitamins and minerals but also encourages the proliferation of advantageous bacteria in your intestine. Try incorporating leafy greens like spinach or kale into smoothies or salads; colorful bell peppers can be added to stir-fries or enjoyed raw with hummus.
Eat legumes like beans and lentils
You need to know how to feed your gut microbiome. Legumes such as beans and lentils are rich in dietary fiber, which serves as fuel for good bacteria residing within our gastrointestinal tract. Incorporate them into soups, stews, or chili dishes.
Consume fruits rich in antioxidants and vitamins
Fruits offer numerous health benefits due to their high content of antioxidants, vitamins, and natural sugars that feed friendly microbes living inside us. Berries are particularly potent sources.
Add herbs and spices to enhance flavor while boosting health benefits
Herbs and spices not only add delicious flavors to our meals but also contain powerful compounds with numerous health benefits. Incorporate them into your cooking routine by adding fresh basil or parsley to salads, sprinkling cinnamon on oatmeal, or using turmeric in curry dishes.
Avoid Highly Processed Foods
Minimizing the consumption of highly processed foods can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome. These products often contain high sugar content or artificial additives that may tip the balance towards disease-promoting microbes. Focus on whole food options instead to support overall gut health.
Limit intake of sugary snacks and beverages
Rampant consumption of sugary snacks and beverages can lead to an imbalance in your gut bacteria, as these sugars provide sustenance for harmful microbes, allowing them to thrive. To keep your gut flora healthy, opt for naturally sweet alternatives like fresh fruits or dried fruit without added sugars. Also, consider replacing soda with water infused with lemon, cucumber, or mint.
Choose natural alternatives over artificially flavored items
Many food items with artificial flavors can disrupt the microorganisms in your gut, potentially causing sickness. Instead, choose natural flavor enhancers such as herbs and spices when cooking at home.
Opt for whole grains instead of refined carbohydrates
- Brown rice: Rich in fiber and nutrients essential for maintaining a healthy microbiome composition.
- Oats: Contain soluble fiber called beta-glucan, which helps feed beneficial bacteria while lowering cholesterol levels.
- Buckwheat: An excellent gluten-free alternative, providing prebiotic fibers that support good bacteria growth in the small intestine.
- Quinoa: A complete protein source with a diverse range of nutrients to promote a balanced diet and overall gut health.
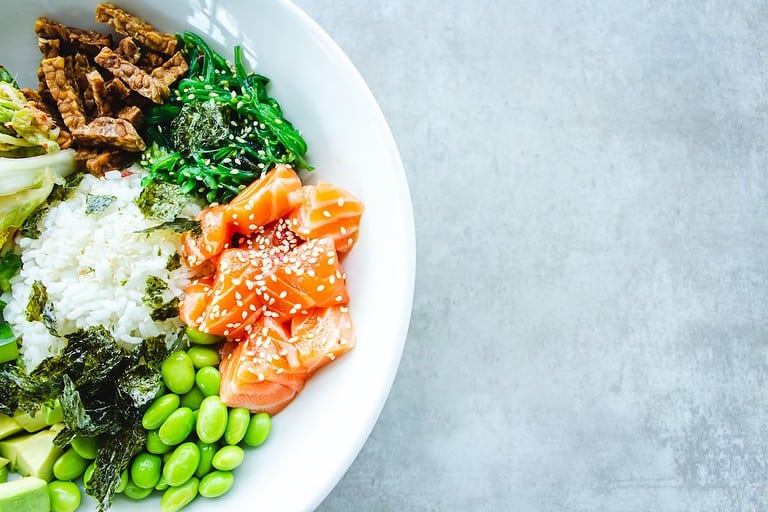
Incorporate Fermented Foods into Your Diet
Fermented foods are known to increase immune system efficiency as well as enhance overall microbial diversity within our gastrointestinal tract. Regularly consuming these probiotic-rich foods can contribute significantly to improving your gut microbiome’s composition. Let’s explore some delicious fermented food options that you can easily incorporate into your daily meals.
Enjoy Plain Yogurt with Fresh Fruit Toppings
Yogurt, preferably plain with minimal added sugars, is a popular and versatile option for boosting gut health. It contains live bacteria cultures that promote a healthy balance of microbes in the digestive system. To make it more enjoyable, try adding fresh fruit toppings like berries or sliced bananas for natural sweetness and extra nutrients.
Experiment with Kimchi or Sauerkraut in Salads or Sandwiches
Kimchi, a Korean fermented cabbage dish, and sauerkraut, its German counterpart, are both excellent sources of probiotics that help maintain optimal gut health. Adding kimchi and sauerkraut to salads or sandwiches can provide essential vitamins, minerals, and probiotics that help maintain gut health.
Sip on Kombucha or Kefir as Refreshing Probiotic Drinks
If you’re looking for something refreshing yet beneficial for your gut microbiome, kombucha (a fizzy tea beverage made using fermentation) and kefir (a fermented milk drink) are great options. Both drinks contain a variety of live bacteria cultures that support gut health, improve digestion, and boost the immune system.
FAQs in Relation to How to Feed Your Gut Microbiome
How do you feed microbes in your gut?
Maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbes is key to overall health and well-being. Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and tempeh contain probiotics – beneficial bacteria that can contribute to a healthy gut microbiome.
Prebiotics are dietary fibers that feed probiotic bacteria already present in the digestive tract. Foods such as bananas, onions, garlic, oats, and apples contain prebiotics. Lastly, staying hydrated is important to ensure the gut environment remains optimal for microbial growth.
What is the best food to heal the gut microbiome?
Optimal nutrition for gut health can be attained through probiotic-rich edibles, prebiotics, and fermented foods. Probiotics are live bacteria found in certain yogurts and other cultured dairy products that can help restore balance to the digestive system. Prebiotics are plant fibers that feed beneficial bacteria already present in the gut.
Consuming fermented food items such as kimchi, sauerkraut, miso soup, kefir, and tempeh can provide beneficial microorganisms for the gut that support healthy digestion. Eating these types of food regularly will provide essential nutrients needed to promote optimal health of your gut microbiome.
Conclusion
By following the steps outlined above, you can help to feed your gut microbiome and support its health. Incorporating a range of fiber-filled eats, adding probiotics and prebiotics as needed, managing stress levels or getting ample rest, plus taking into account environmental elements that could be affecting your digestive system, are all key for keeping gut health in check. Taking these measures will ensure that you have a thriving gut microbiome essential for overall well-being.
Take charge of your health and well-being by learning how to feed your gut microbiome for optimal digestive function. With our resources at Smart Living Now, you can make smart lifestyle choices that will benefit the entire family now and in the future.